Ability to return result sets from triggers is one of the features that is marked as a deprecated feature in SQL Server 2012.
After reading this, few questions flashed my mind, that I would like to share with you.
- How do we return the result sets from triggers?
- Why do we need this feature mostly?
- How can we stop using this feature from earlier versions?
- How can we get the same functionality without using this feature?
I added first two questions for the beginners to understand this concept.
Lets proceed step by step from the first question.
- How do we return the result sets from triggers ?
Step 1 :
Lets create a table to demonstrate the use of return the result sets from trigger.
USE tempdb; GO CREATE TABLE tbl_Employee( EmployeeID int identity (1,1), EmployeeName nvarchar(100) NULL ) GO
Step 2 :
Create a trigger on this table (tbl_Employee).
CREATE TRIGGER trg_Insert ON tbl_Employee FOR INSERT AS SELECT INSERTED.EmployeeID, INSERTED.EmployeeName FROM inserted; GO
Step 3 :
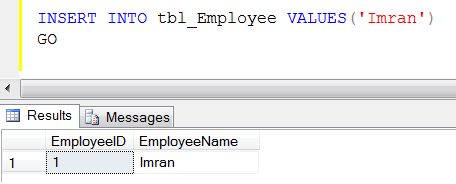
Now, lets insert one record and check if it is working properly.
INSERT INTO tbl_Employee VALUES('Imran')
GO
--OUTPUT
Woww, it is working, we got the result sets from the trigger 😉
- Why do we need this feature mostly?
Mostly, we use select statement inside the trigger/ stored procedure to return the result set and the purpose of the result set is to debug (to check what values it returns) the trigger / stored procedure.
(Note : It is a common practice to debug any trigger/stored procedure via result set, but it may break your application and also it is not recommended).
- How can we stop using this feature from earlier versions?
Step 4 :
We are enabling an advance feature ‘disallow results from triggers’ to 1 to enable this feature in the earlier version of SQL Server and it is also recommended by SQL Server to make it 1.
sp_configure 'disallow results from triggers',1 GO RECONFIGURE
Step 5 :
Insert one more record in the table after enabling the feature and check that this feature has enabled properly or not.
INSERT INTO tbl_Employee VALUES('Bob')
GO
--OUTPUT
Ooopps…… I am unable to execute it, because I enabled the return result set feature from trigger at instance level not on database level
and it is working fine.
Msg 524, Level 16, State 1, Procedure trg_Insert, Line 4
A trigger returned a resultset and the server option ‘disallow_results_from_triggers’ is true.
- How can we get the same functionality without using this feature?
Step 6 :
You can easily use the same functionality without using this feature. Let me alter the trigger and make a sample.
ALTER TRIGGER trg_Insert ON tbl_Employee FOR INSERT AS Declare @EmployeeID int Declare @EmployeeName nvarchar(100) SELECT @EmployeeID=INSERTED.EmployeeID , @EmployeeName=INSERTED.EmployeeName FROM inserted; Print 'EmployeeID ' + Convert (varchar(10),@EmployeeID) Print 'Employee Name ' + @EmployeeName GO
Step 7 :
Insert one more record in the table and check the functionality.
INSERT INTO tbl_Employee VALUES('Sandra')
GO
--OUTPUT
EmployeeID 3
Employee Name Sandra
Conclusion :
DO NOT use SELECT statement to return the result set from a stored procedure / trigger. Always use print command instead, to debug it.
Reference : MSDN