How to convert Gregorian date format to simple Hijri date format? Doesn’t it sound a very simple question? Yes, because in the earlier versions of SQL Server you could convert Gregorian dates to simple Hijri date format (dd mon yyyy hh:mi:ss:mmmAM). But if you need to convert Gregorian dates to any specific Hijri date format, then comes the problem. Basically, the earlier version of SQL Server supports very limited type of Hijri date formats but in SQL Server 2012, you can convert Gregorian dates to ANY Hijri date format using FORMAT function.
Let me convert it using different methods :
Method 1 : Using Convert Function
--This script is compatible with SQL Server 2005 and above. --This Method can convert into very limited format of Hijri dates. DECLARE @DateTime AS DATETIME SET @DateTime=GETDATE() SELECT @DateTime AS [Gregorian Date] , CONVERT(VARCHAR(11),@DateTime,131) AS [Gregorian date to Hijri date] GO --OUTPUT
Method 2 : Using Format Function
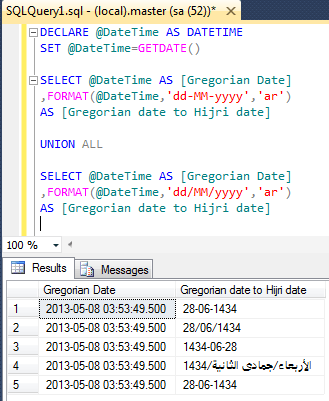
--This script is compatible with SQL Server 2012 and above. DECLARE @DateTime AS DATETIME SET @DateTime=GETDATE() SELECT @DateTime AS [Gregorian Date] ,FORMAT(@DateTime,'dd-MM-yyyy','ar') AS [Gregorian date to Hijri date] UNION ALL SELECT @DateTime AS [Gregorian Date] ,FORMAT(@DateTime,'dd/MM/yyyy','ar') AS [Gregorian date to Hijri date] UNION ALL SELECT @DateTime AS [Gregorian Date] ,FORMAT(@DateTime,'yyyy-MM-dd','ar') AS [Gregorian date to Hijri date] UNION ALL SELECT @DateTime AS [Gregorian Date] ,FORMAT(@DateTime,'dddd/MMMM/yyyy','ar') AS [Gregorian date to Hijri date] UNION ALL SELECT @DateTime AS [Gregorian Date] ,FORMAT(@DateTime,'dd-MM-yyyy','ar') AS [Gregorian date to Hijri date] GO --OUTPUT
Let me know if you know any better way.