In my earlier article, I wrote about the new feature of SQL Server 2012 namely Insert Snippet. This is quite a handy feature which can save a lot of your time. This feature is shipped with a lot of standard objects snippet with the customization options.
But there were two big questions in front of me. 1) Why do we need to customize it? 2) How can this save our time ?
Answer :The reason for customization is that, each and every company follows some standards to create standard object (Table, view etc.) of SQL Server. For example the name of the table should start with tbl_ or there might be some additional fixed column with some default values in each table etc etc. Therefore, once you customize the snippet as per your requirements, then you can use it every time.
Prerequisite: How to insert the Snippet in SQL Server 2012.
Solution :
Let me explain, how to customize the standard object table snippet Step by Step :
Step 1 :
First of all, I will take you to the path where snippet of the standard objects resides in the SQL Server 2012.
To find the path you need to go to Tools and select Code Snippets Manager as shown in the picture below.
Once you open the Code Snippets Manager, select the appropriate object and you can see the path of that particular object as shown in the picture below.

Step 2 :
As you can see the path of table snippet in the above picture, the next step is to browse the table path and find the standard table snippet namely Create Table.snippet.
Step 3 :
Now, you are in the standard table snippet folder, so you need to make a copy of the standard table object namely “Create Table.snippet” and rename it to “Create Sample Table.snippet” as shown in the picture below.
Step 4 :
Open the newly created file Create Sample Table.snippet, first and foremost, change the title as highlighted in the given below picture.
Step 5 :
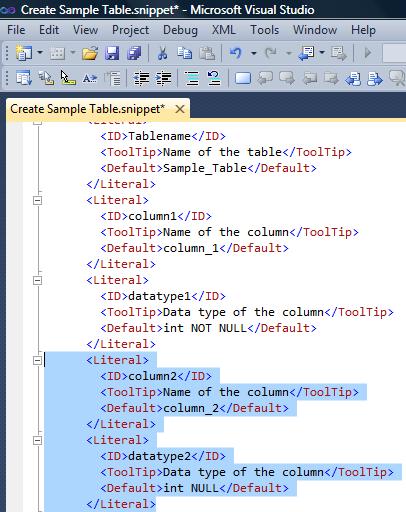
Once you change the title copy the selected area as shown in the picture below and paste twice after <Literal> because we need to add two additional columns of the table in the snippet.
Step 6 :
Lets rename the column name and data type of the columns ([Creation_Datetime] & [Created_By] having data type datetime and nvarchar(50) respectively as shown in the picture below.
Step 7 :
Once you create the additional column, do not close the file, just scroll down a little bit in the same file and copy the selected area ($Column2$ $datatpe2$) and paste it twice and then rename it to $column3$ & 4$ and $datatype 3$ & 4$ respectively as shown in the picture below.
Step 8 :
Once all the changes are done in Create Sample Table.snippet save and close the file and open SQL Server Management Studio.
Step 9 :
Lets insert the customized table snippet in Query window as shown below.