File table is one of my favorite features introduced in SQL Server 2012. When I was working with file table, I came across a question how to find all system objects (primary key, default vaule, indexes etc) related to any file table.
We can achieve this by two different methods.
Method 1:
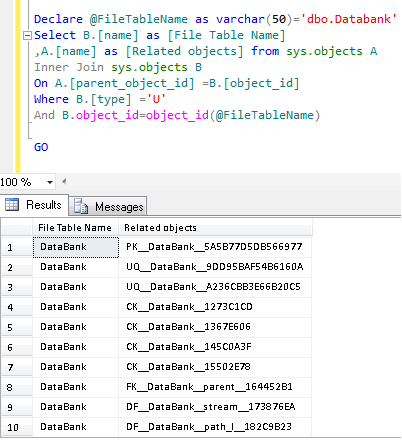
In this method, we did self-join in the sys.objects to find all system objects related to any file table. This is general script that we normally use to find any child object related to parent object.
--This script will work in SQL Server 2012 and above. Declare @FileTableName as varchar(50)='dbo.Databank' -- Enter File table Name Here Select B.[name] as [File Table Name] ,A.[name] as [Related objects] from sys.objects A Inner Join sys.objects B On A.[parent_object_id] =B.[object_id] Where B.[type] ='U' And B.object_id=object_id(@FileTableName) GO --OUTPUT
Method 2 (Shortcut):
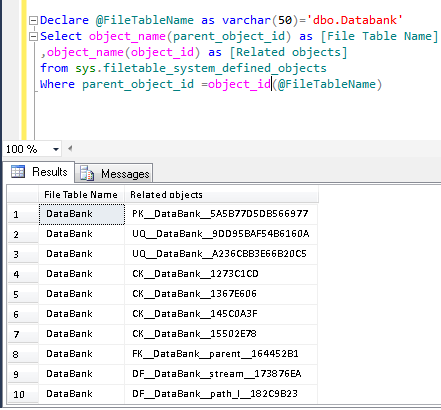
In this method, we used a new system view namely sys.filetable_system_defined_objects (This system view returns all the system objects related to any file table) introduced in SQL Server 2012.
Given below is the script that will give you all system objects related to file table without any self-join.
--This script will work in SQL Server 2012 and above. Declare @FileTableName as varchar(50)='dbo.Databank' Select object_name(parent_object_id) as [File Table Name] ,object_name(object_id) as [Related objects] from sys.filetable_system_defined_objects Where parent_object_id =object_id(@FileTableName) GO --OUTPUT
Aware of any other shortcut ?