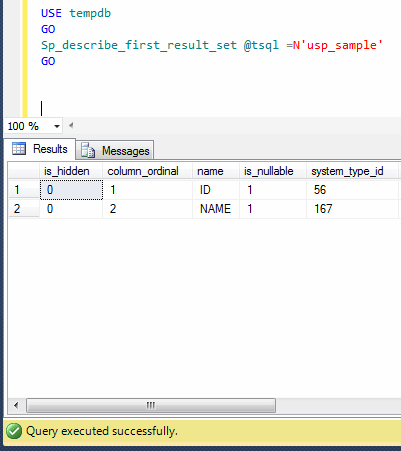
Today, I installed a SQL Server instance in one of my labs, and tried to run a query using OPENROWSET and got an error. Given below are the details of the error.
Message Number: 15281
Severity : 16
Error Message: SQL Server blocked access to %S_MSG ‘%ls’ of component ‘%.*ls’ because this component is turned off as part of the security configuration for this server. A system administrator can enable the use of ‘%.*ls’ by using sp_configure. For more information about enabling ‘%.*ls’, see “Surface Area Configuration” in SQL Server Books Online.
Error Generation:
Given below is the script that I tried to execute but it resulted with the following error:
USE AdventureWorks2012
GO
SELECT *
FROM OPENROWSET('SQLNCLI', 'Server=(local);uid=test;pwd=test',
'EXEC AdventureWorks2012.[dbo].[uspGetManagerEmployees] 16');
Msg 15281, Level 16, State 1, Line 1
SQL Server blocked access to STATEMENT ‘OpenRowset/OpenDatasource’ of component ‘Ad Hoc Distributed Queries’ because this component is turned off as part of the security configuration for this server. A system administrator can enable the use of ‘Ad Hoc Distributed Queries’ by using sp_configure. For more information about enabling ‘Ad Hoc Distributed Queries’, search for ‘Ad Hoc Distributed Queries’ in SQL Server Books Online.
Ooopps…… I am unable to execute the OPENROWSET query.
Resolution:
Basically, ‘Ad hoc Distributed Queries’ are disabled by default in SQL Server due to security configuration and you cannot use either OPENROWSET or OPENDATASOURCE and if you cannot execute these two rowset functions, then you cannot access any remote data sources. So how to fix this issue?
Given below is the script to enable ‘Ad hoc Distributed Queries’.
USE master GO sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1; RECONFIGURE; GO sp_configure 'Ad Hoc Distributed Queries', 1; RECONFIGURE; GO --OUTPUT
Configuration option ‘show advanced options’ changed from 0 to 1. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install.
Configuration option ‘Ad hoc Distributed Queries’ changed from 0 to 1. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install.
As you can see above, the ‘Ad hoc Distributed Queries’ setting changed from 0 to 1. Now you can easily execute any ‘Ad hoc Query’
Note : By default, this option is set to 0 and you need to change it to 1 to activate this feature.