‘Can you restore SQL Server 2012 backup in earlier versions of SQL Server?’ I came across this question many times from the community and the simple answer is NO. You cannot restore a new version of SQL Server backup in earlier versions. However, there is a way around that can be followed to achieve it. Basically, you can generate the script of all objects along with the data using SQL Server 2012 with any earlier versions compatibility and run those scripts on earlier versions of SQL Server. This is how you can get the complete data with schema from SQL Server 2012 to earlier versions.
Problem :
Before proceeding with the solution, I would like to show you the error, that happens when you restore a higher versions of
SQL Server database backup to an earlier version of SQL Server. Given below is the image.

The media family on device ‘E:\DBBackup\AdventureWorks2012_Backup\AdventureWorks2012_Backup’ is incorrectly formed. SQL Server cannot process this media family.
RESTORE HEADERONLY is terminating abnormally. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 3241)
SOLUTION :
Let me proceed with the solution, step by step.
Step 1:
Open SSMS and right click on the database that you want to restore in earlier versions of SQL Server and then select Task and then further click on Generate Script …
Given below is the image.

Step 2 :
Given below is the informational screen, that will guide you how to generate the scripts along with the steps. Press NEXT button.

Step 3 :
In this step, you will get two options. Given below are the details.
- Script entire database and all database objects
- Select specific database objects
Option 1 is preferred because you can generate all database objects altogether from it. However if you upgrade any object using any new features of SQL Server 2012, then you should select Option 2 and exclude that particular object and press NEXT button. Given below is the screen image.

Step 4 :
In this option you need to select the script file location to save all the scripts in a particular file. Rest of the options you can leave as default. Once you are done with the file location, you can see an ADVANCE button. Click on this button. It will open the advance option for the scripting.

Step 5 :
Once you are inside the Advance option, you need to select further two options. Given below are the details.
- Script for SQL Server version
- Type of data to script.
In the Option 1 make sure that you have selected the right earlier Version of SQL Server, as shown in the image below.

In the Option 2, make sure that you have selected Schema and data, as shown in the image below.
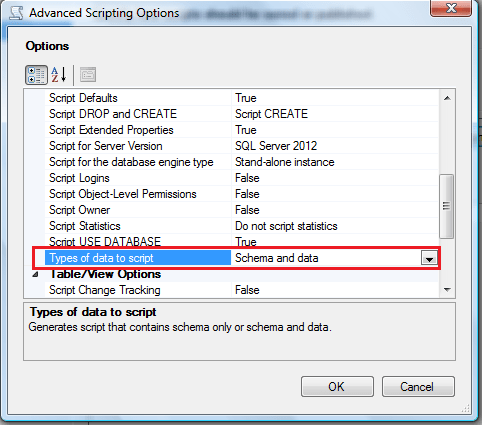
Once you configure both options, press OK and press Next in the previous screen, as shown below.

Step 6
Once you press NEXT button, it will take you to the summary screen where you can see all your configuration altogether.
Again press NEXT button to proceed, as show in the image below.

Step 7
In this step, SQL Server will automatically script all your selected object along with the data. And will give you the status report, as shown in the image below.


Step 8 :
Now you need to browse the file you saved in particular location in the Step 4 and Execute it in selected earlier version of SQL Server.
Let me know if you came across this problem and resolved it in a different manner.
Read Full Post »