In my previous article I discussed about CUME_DIST. In this artcile we will discuss another important analytical function introduced in SQL SERVER 2012 and that is similar to CUME_DIST namely PERCENT_RANK. Lets discuss PERCENT_RANK syntax, purpose, return type, simple examples.
Syntax
PERCENT_RANK( )
OVER ( [ partition_by_clause ] order_by_clause )
Purpose
The purpose of this function is to calculate the relative rank of a row within a group of rows. PERCENT_RANK of any set of First row value will be 0. PERCENT_RANK includes NULL values but they are treated as the lowest possible values.
Return Type
The return type is float(53) and the values are always between 0 and 1.
Example 1 : Simple PERCENT_RANK()
Lets take gold rates as an example to check their relative rank in one week.
Create table [Daily_Gold_Rate]
(
(
[S.No] int,
[Date] datetime,
[Carat] int,
[Gold Rate] numeric(18,2)
)
Insert into [Daily_Gold_Rate] values(1,'2013-01-03',18,155.00)
Insert into [Daily_Gold_Rate] values(4,'2013-01-04',18,153.00)
Insert into [Daily_Gold_Rate] values(7,'2013-01-05',18,152.00)
Insert into [Daily_Gold_Rate] values(10,'2013-01-06',18,154.50)
Insert into [Daily_Gold_Rate] values(13,'2013-01-07',18,154.50)
GO
Select
Row_Number() OVER (ORDER BY [Carat],[Gold Rate]) as [Row Number]
,[Date]
,[Carat]
,[Gold Rate]
,PERCENT_RANK () OVER (ORDER BY [Carat],[Gold Rate]) AS [PERCENT_RANK]
from [Daily_Gold_Rate]
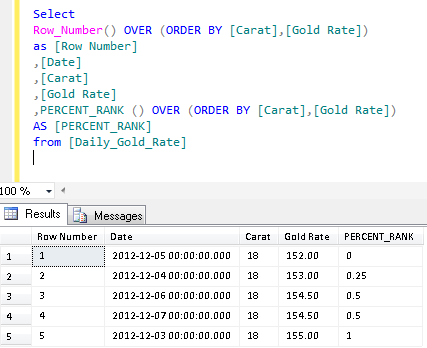
Explanation :

If you look at Column E and Column H, Column E is calculated by SQL Server and Column H is calculated manually to understand how it works. To calculate PERCENT_RANK() manually, you need two values.
1. Row Number based on the values (meaning less than or equal to value) (Column F). But first value will always be 0.
2. Total Number of Records – 1 (Column G)
Column G: It is simple; you need to calculate the total number of records and reduce 1 from it.
Column F: You simply need to get the row number based on the values. But first row number will be 0 as well, so you need start counting it from row number 2. You can observe that it is simple row number till row number 2 but in row number 3 & 4 we found the same Gold rate, so it picked up 2 (due to less than or equal to value criteria) as row number.
Finally, you need to divide Column F by Column G to get the PERCENT_RANK() manually. The same functionality PERCENT_RANK() does automatically in SQL.
Example 2 : PERCENT_RANK() with Partition By Clause
Lets insert other Gold rates to proceed with this example.
Insert into [Daily_Gold_Rate] values(2,'2013-01-03',22,190.50)
Insert into [Daily_Gold_Rate] values(3,'2013-01-03',24,202.23)
Insert into [Daily_Gold_Rate] values(5,'2013-01-04',22,191.00)
Insert into [Daily_Gold_Rate] values(6,'2013-01-04',24,202.25)
Insert into [Daily_Gold_Rate] values(8,'2013-01-05',22,190.00)
Insert into [Daily_Gold_Rate] values(9,'2013-01-05',24,203.25)
Insert into [Daily_Gold_Rate] values(11,'2013-01-06',22,189.50)
Insert into [Daily_Gold_Rate] values(12,'2013-01-06',24,201.50)
Insert into [Daily_Gold_Rate] values(14,'2013-01-07',22,189.00)
Insert into [Daily_Gold_Rate] values(15,'2013-01-07',24,201.00)
Select
Row_Number() OVER (Partition by [Carat] ORDER BY [Carat],[Gold Rate])
as [Row Number]
,[Date]
,[Carat]
,[Gold Rate]
,PERCENT_RANK () OVER (Partition by [Carat] ORDER BY [Carat],[Gold Rate])
AS [PERCENT_RANK]
from [Daily_Gold_Rate]

Reference :MSDN
Read Full Post »