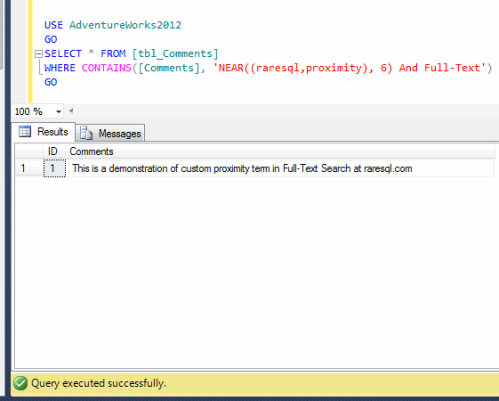
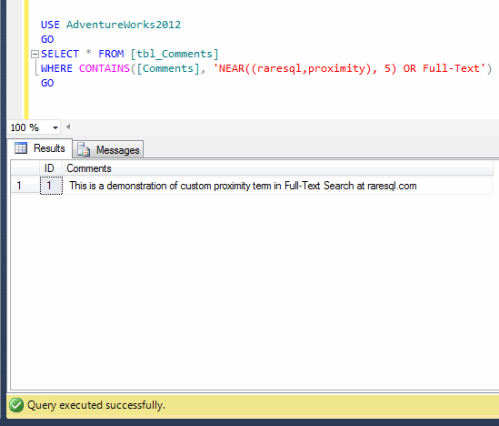
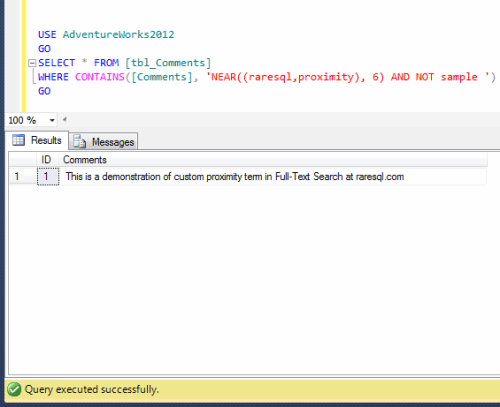
This is a very common issue, when you work on long running queries or procedures, and the PROBLEM is that you need to check the stored procedure from time to time whether it has been executed successfully or failed or it is still running. Sometimes you are busy with some other stuff and you forget to check the status. I came across this scenario many times specially, when I am working on parallel projects and each of them taking time specially if it is a migration and the database size is too big.
Let me demonstrate step by step, how I resolved the issue and made my life easier.
Step 1 :
First of all you need to configure the database mail in each SQL Server using this article and make sure that is working.
Step 2 :
You need to alter your stored procedure and add few additional scripts. These additional lines of script are basically the TRY…CATCH block and sp_send_dbmail to send Email in case of success or failure. Whenever, the procedure will come across any error or if it is executed successfully, it will generate an email and notify the admin. In addition you can format the email and add any additional information that can help you to trace the error.
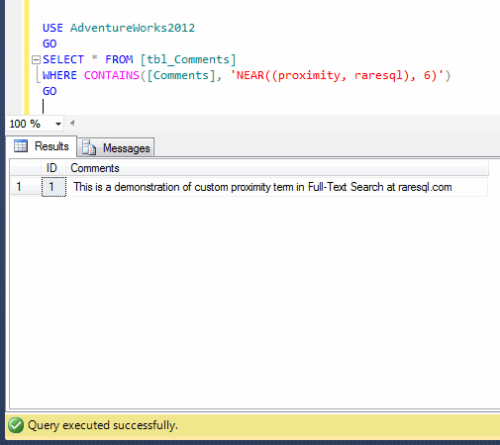
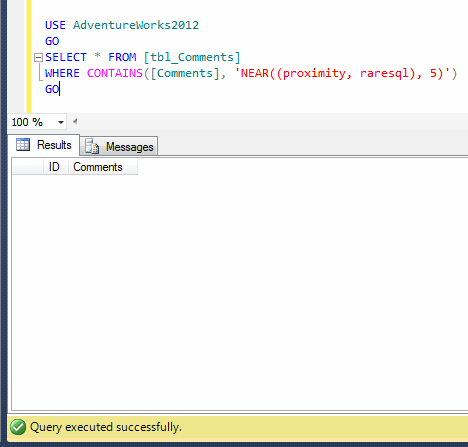
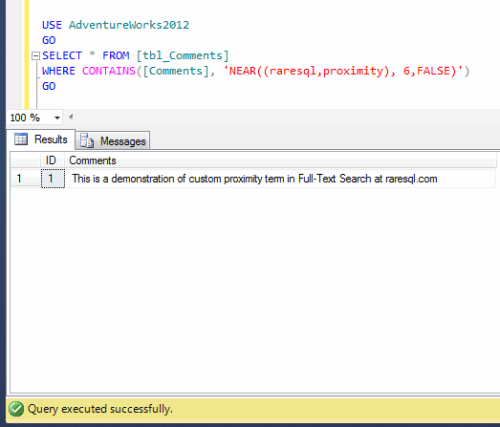
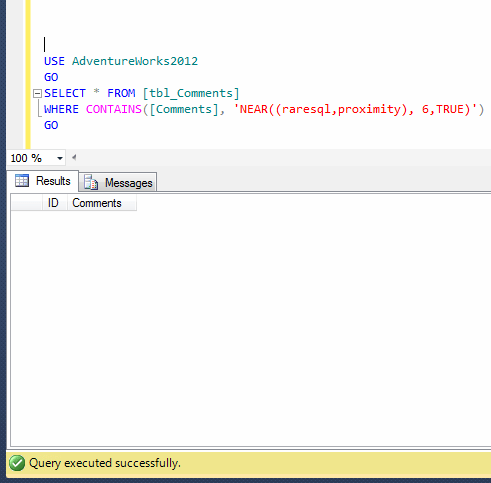
Given below is the sample script in which I created a table and inserted records using stored procedure and generated an email whether it has been executed successfully or failed.
This script may take few minutes to execute.
--This script is compatible with SQL Server 2005 and above.
USE tempdb
GO
DROP TABLE tbl_sample
GO
--Create Sample table
CREATE TABLE tbl_sample
(
[ID] INT IDENTITY(1,1),
[Name] varchar(10)
)
GO
--DROP PROCEDURE usp_test
--GO
--Create sample stored procedure
CREATE PROCEDURE usp_test
AS
BEGIN TRANSACTION;
BEGIN TRY
DECLARE @int INT
SET @int = 1
WHILE (@int <=400000)
BEGIN
INSERT INTO tbl_sample VALUES ('Test')
SET @int = @int + 1
END
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
IF @@TRANCOUNT > 0
BEGIN
DECLARE @ErrorMessage NVARCHAR(4000);
DECLARE @ErrorSeverity INT;
DECLARE @ErrorState INT;
SET @ErrorMessage = 'Dear Admin,<BR><BR>Due to some error
, your procedure ''usp_test'' at Server ' + @@Servername +
' has been rollback.<BR>'
+ 'Given below is the error message.
<BR><BR> ErrorMessage : ' + ERROR_MESSAGE()
ROLLBACK TRANSACTION;
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail @profile_name='My Profile',
@recipients='admin@raresql.com',
@subject='Procedure Failed & Rollback',
@body= @ErrorMessage,
@body_format = 'HTML',
@execute_query_database = 'tempdb'
END
END CATCH;
IF @@TRANCOUNT > 0
BEGIN
COMMIT TRANSACTION;
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail @profile_name='My Profile',
@recipients='admin@raresql.com',
@subject='Procedure Executed Successfully',
@execute_query_database = 'tempdb'
END
GO
--Execute the Stored Procedure
EXEC usp_test
GO
I found it very handy, let me know if you come across this issue and its resolution.