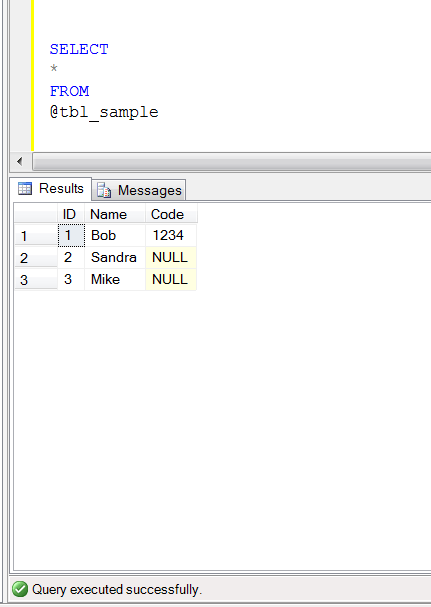
Mostly companies develop several environments from development stage till production like Development environment, Integration environment, Validation environment, Quality Assurance environment, User Acceptance environment and Production environment to enhance quality of the product for the customer. But once we have different environments, there is a very common issue called inconsistency in database between these environments. Sometimes, script manager may miss out some scripts to deploy, and due to this one or all of the environments can create serious problems and may crashes also. And if this is user acceptance / production environment, it may create a cumbersome image about your product. Sometimes, we use user defined functions and stored procedures to compare two databases like this. However, I felt that these solutions are good, it can help you how to fix, but it is not a smart solution (can automatically fix the issues).
Recently, I came across an issue where we have many environments and in all different environments it was generating different database inconsistency errors. So I started doing my research, and came across a tool namely ApexSQL Diff, a schema comparison tool. I tested this tool and I synced all environments in a very few minutes with just a few clicks. My customer was damn happy and was inquiring how I managed to do it in few minutes as it seems, it takes few weeks to sort out. I recommended this solution to the customer & exclaimed,”it is money’s worth”. I approached APEX team to purchase this product for my customers & get some discount, so thought of getting same discount for my blog reader. And finally I got it :). You can use coupon Code ApexSQLDiffPro25 to get 25% discount on APEXSQL Diff.
Note : There is a FREE community version of ApexSQL Diff for SQL Express and Windows Azure SQL Databases.
Let me explain step by step how it works.
STEP 1:
Once you open ApexSQL Diff, click on New button, it asks about source and destination of your SQL server database (Backup, Script folder, Snapshot, Source control) to compare as shown in the image below.

STEP 2:
Once you select source and destination databases to compare, just press Compare button at the bottom of the screen. It takes a while and it will give you all schema differences between both databases. It supports new object shipped with SQL Server 2012 as well, as shown in the image below.

It also provides additional sorting, formatting (alignment & grouping) and filter options like object filter, difference filter & script difference view to give you full control over differences, as shown in the image below.

STEP 3:
Once you have the differences, just press Sync button and it can sync both databases and can give you the script also (in case you want to deploy by yourself), as shown in the picture below.

Last but not least, it does not stop working here, it syncs again to check if you missed to upgrade/update any scripts and gives you the difference (if any).
I like this product and I also recommend that you should try and view its results by yourself. Its trial version is available here.
You can get further details about the product from http://blog.apexsql.com/category/apexsql-diff/. Let me know your opinions whether positive or not.
Read Full Post »