Database mail is one of the best features shipped in SQL Server 2005. It allows us to send mails without writing even a single line of script. However, there is a general perception that you must have your own mail server to configure Database Mail in the SQL Server and frankly speaking, to configure a mail server, a good amount of expertise is required. Due to the lack of expertise in mail server configuration in new bie of SQL Server, they usually avoid learning, testing and implementing this nice feature.
However, one of the benefits of SQL Server Database mail is that, it is NOT mandatory that you must have your own mail server, you can easily configure, test and implement it on any FREE mail servers like Gmail, Yahoo & Hotmail etc. and it is just a matter of few clicks.
In this article, I will demonstrate step by step how to configure & test SQL Server database mail using Gmail, Yahoo & Hotmail accounts.
Before proceeding with the configuration, please make sure that you HAVE a valid email account in any of the FREE mail servers.
STEP 1 – Navigate to Database Mail:
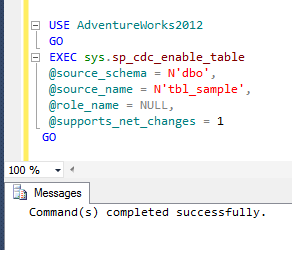
First of all, you need to open SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and select Object Explorer followed by Management node and then Database Mail as shown below.

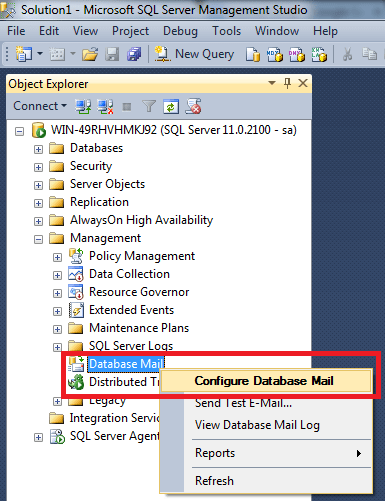
STEP 2 – Configure Database Mail:
Once you select Database Mail, just right click on it and select Configure Database Mail as shown below.
STEP 3 – Welcome Screen:
Now, you are in welcome screen. This screen tells you all about Database Mail. However, you can check “skip the page in the future” in order to avoid this screen next time. Just Press NEXT button to proceed as shown below.

STEP 4 – Configuration Task:
Next step is to create a new profile and then you can add multiple Email accounts in it in the later steps. In order to create a new profile you should select Option 1 (Set up Database Mail by performing the following tasks ) and press NEXT button as shown below.

STEP 5 – Enable Database Mail Feature:
Once you press Next button in the above step, it may ask you to Enable the Database Mail feature. It happens only when you configure the database mail for the first time. Click Yes and then Press NEXT to proceed.

STEP 6 – Profile Creation:
Once you enable the database mail, it will take you to the profile creation screen, where you can create a new profile as shown below. In this screen you can enter a unique profile name and a description (NOT mandatory), which is just an explanation to your profile. Once you are done with this information, just click Add button in order to add an Email account in the profile.

STEP 7 – Mail Account Creation:
Now you are in the Email account creation screen as shown below. You should be very careful to enter the data in this screen because your one typo mistake will STOP Database mail to send any email. The most important data that you must enter in this screen is its Server name (Actually SMTP Server name). In addition, you can use the Port No 25 but sometimes this port is blocked in your network. If you come across this situation, you can change the port number from 25 to 587.
Given below are the SMTP addresses of the FREE mail accounts.
- Yahoo : smtp.mail.yahoo.com
- Gmail : smtp.gmail.com
- Hotmail : smtp.live.com
Below are the configurations for each mail account, however, you will use one/all of them. In addition, you need to make sure that your email credentials IS correct.
Yahoo account configuration :

Gmail account configuration :

Hotmail account configuration :

STEP 8 – Profile Verification:
Once you are done with the email account press OK button and it will take you back to the profile screen and it adds the email account, you just configured it in STEP 7 in the profile as shown below. Press NEXT button to proceed.

STEP 9 – Profile Security:
Now you entered into the manager profile security screen, you need to be very careful when configuring profile security. However, for testing purpose you can make it Public and default profile as well, as shown below and Press NEXT button.

STEP 10 – System Parameters:
This screen will show the configuration of system parameters as shown below, you just need to press NEXT button to proceed.

STEP 11 – Completion:
Now, you are in the database Mail complete wizard, this screen will show you a summary of all your configuration, if you find any mistake even in this step, you can press BACK button and correct. However, if each and every configuration is correct, press FINISH button to complete the database mail configurations.

STEP 12 – Status:
Once you press FINISH button in the above step, it will show you the status of the database mail configuration as shown below. It can be either be a success or a failure.

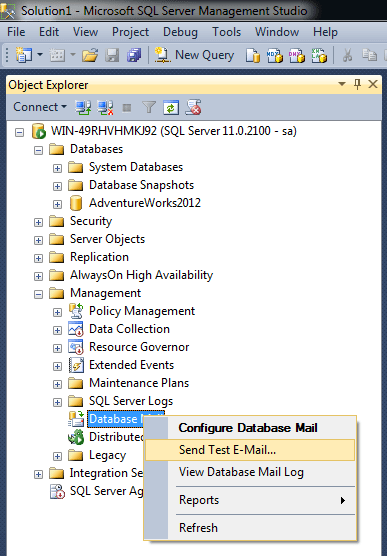
STEP 13 – Browse Send Test Email:
Lets test the database mail whether it is working fine or not. You need to again select the Database email and right click on it to further select the Send Test E-Mail.. as shown below.
STEP 14 – Send Test Email:
Once you select the Send Test E-Mail.., it opens a test email creation screen, where you will find your default profile to be selected. You just need to type any valid email address in the To where you want to send a test mail. In addition, you can change the subject and body as well and press the Send Test E-Mail button. The moment you press this button, you will receive (Depends upon the server configuration) the test email in that defined email address from your Gmail, Yahoo or Hotmail account whichever you configured above in the selected profile.

Let me know if you configured Database and faced any particular issue in setting it up.
Read Full Post »